Integrated-whole-person care requires integrated-whole-person data, yet most healthcare data is scattered across disparate sources. Even when behavioral health organizations and Independent Practice Associations (IPAs) make large financial investments into data platforms and the IT resources to operate them, those products are limited in interoperability, and staff find themselves spending significant time extracting, cleaning, and synthesizing data to answer pertinent business questions. As a result, organizations can find it challenging to identify which subpopulations are in need of targeted and timely interventions.

Pamela Mattel, LCSW
Behavioral health organizations, Certified Community Behavioral Health Clinics (CCBHCs), and Independent Practice Associations (IPAs) aim to understand the impact of their care delivery at every stage and identify opportunities for improvement. Accordingly, they must aggregate data in pursuit of a holistic patient record. However, these efforts are often stymied by the inherent messiness of healthcare data, which includes inconsistent formats, incomplete records, little standardization across sources, or lack of access to such data. Complex concerns around patient security and privacy through layered consent processes are a further complication.
Coordinated Behavioral Care (CBC) recognized that the lack of data integration along the person’s health journey made it difficult to deliver comprehensive, effective, and timely care. Given its mission to empower underserved populations, who already face significant barriers to accessing care, CBC knew it needed to address these challenges without adding significant administrative burden or cost.
To achieve this, CBC partnered with Informd—an IT and data consultancy—to embark on its strategic plan for business intelligence (BI). In this article, the authors share why CBC undertook this journey, the results to date, and future ambitions.
CBC is a clinically integrated network of NYC’s most forward-thinking not-for-profit health and human services agencies, delivering what matters most to over 150,000 people every year. These essential and extensive services—behavioral health, primary care, care coordination, housing, and other social care services—are improving the lives of individuals and families facing some of the most challenging issues with client-centered, data-informed, best practice approaches.
Collectively, these 77 agencies comprise the CBC Independent Practice Association and Health Home, which serves adults and children in New York City, Long Island, and Lower Westchester. Together, they are developing and implementing solutions in concert with the broader healthcare system, payors, government, and communities.
CBC orchestrates a sophisticated, complex care ecosystem to improve outcomes. Centralized multidisciplinary staff, including peers, align partners around shared values, operate centralized intake, coordinate outreach and service activities, provide clinical support, case conferences, and training, and generate data-informed quality improvement.
Informd is a New York-based boutique consulting firm, and its advisors are trusted technology partners for many health and human service provider organizations across the New York metropolitan region and beyond. Founded in 2019, Informd’s team of nearly 20 experts have significant experience with and understanding of the complexities of New York’s healthcare, behavioral health, and social service systems and are intimately familiar with the Medicaid redesign and Value-Based Care reforms occurring over the last decade.
Informd has become a trusted advisor and partner to behavioral health IPAs, Behavioral Health Care Collaboratives (BHCCs), and information technology organizations, as well as substance use and mental health provider organizations, housing, criminal justice, and child welfare agencies. Each requires a deep understanding of their unique cultures, circumstances, and challenges.
From Decentralization to ‘One Team’ – Technology as a Catalyst for Culture Change
Prior to undertaking this effort, CBC data staff operated in a siloed capacity, with data analysts reporting on specific programs. Staff were extracting numerous files from the Electronic Health Record (EHR) but lacked repeatable data assets—meaning that each week, month, or quarter, staff had to manually download multiple CSV files and manually knit them together to calculate program outcomes. Each department had a unique process for data collection despite relying on similar data extracts. In short, CBC had neither standardization nor repeatability of data.
Program Directors were forced to handle complex data analysis tasks alongside their data analysts. Often, these staff handled time-consuming tasks such as manually sifting through Excel spreadsheets or using functions like “VLOOKUP” to identify pertinent events, e.g., which individuals were discharged the previous day and therefore needed follow-up care in the coming week. This inefficient process not only took up valuable time but also increased the likelihood of data errors and resulted in poor analytics.
Recognizing these challenges, CBC leadership engaged Informd to assess how CBC’s data resources were organized and develop a structure that resulted in a centralized and cohesive data team. Informd also developed team roles and responsibilities that supported the implementation of a comprehensive Enterprise Data Strategy.
Next, the CBC data team underwent training to increase their technical skills with various data tools. At the same time, Informd began data acquisition efforts with EHR vendors, network agencies, the statewide Health Information Exchange (HIE), and other data suppliers. This resulted in a custom-built, efficient, and effective data infrastructure with real-time data pipelines to CBC’s data warehouse.
The CBC leadership and data teams and Informd staff together identified and assessed data sources and reporting requirements—particularly around the need to gain timely patient care insights. CBC pursued a thorough documentation process that unpacked reporting needs into data sources, business definitions, and key measures of performance. This produced a catalog of current reports and logical reporting models, which were transformed into automations using SQL and presented using Tableau.
The culmination of these efforts was the creation of a data lake, data warehouse, and data model in less than 12 months. This framework now enables streamlined reporting and dashboards, giving CBC insights at their fingertips while also setting the stage for discovery and external data sharing with the CBC network. The result is the ability to see a member’s journey, from referral to successful completion of health and behavioral health interventions. For programs such as CBC’s Health Home, turnaround times for new reports decreased from an average of one week to less than four hours. Health Home documentation compliance can be tracked in near real-time, resulting in a reduction of 2,000 hours per year in manual effort.
CBC envisions future enhancements of adding Social Vulnerability Index metrics and Qualified Health Information Network (QHIN) data to its existing data sets and enabling health equity filters across its reporting. By housing and normalizing all its data in a data warehouse, CBC can apply data science methodology to assess, measure, and report on clinical outcomes. For example, CBC can pinpoint diagnoses that impact poorer outcomes for the member or identify if a member was at risk for hospitalization based on their encounters, thereby making timely decisions—who needs care now and what is the best type of care they could receive to close the gap.
Informd’s Enablement Frameworks
CBC benefited from Informd’s E3 (Extract, Enrich, Empower) data enablement framework which reduces the barriers that most healthcare organizations face when trying to aggregate data by supporting a technical infrastructure with:
- Flexibility: creates a vendor-agnostic architecture that solves the difficulties faced in trying to move data from one product to another.
- Cost management: allows for growth without worrying about per member per month (PMPM) considerations.
- Speed: enables organizations to quickly enhance and upgrade its technology environment to respond to changing business priorities without competing for space on a vendor’s product roadmap.
- Scalability: builds on-demand elasticity without the typical long planning and contracting cycles.
CBC also realized both operational and strategic benefits from employing Informd’s A3 (Analytics, Automation, and AI) framework. Operationally, the organization can generate uniform reporting and deploy dashboards to CBC staff for self-service analytics. In addition, they have automated reporting for payors, state agencies, and internal stakeholders. Strategically, the ability to access reliable, reusable and repeatable reporting aligned with the organization’s business goals.
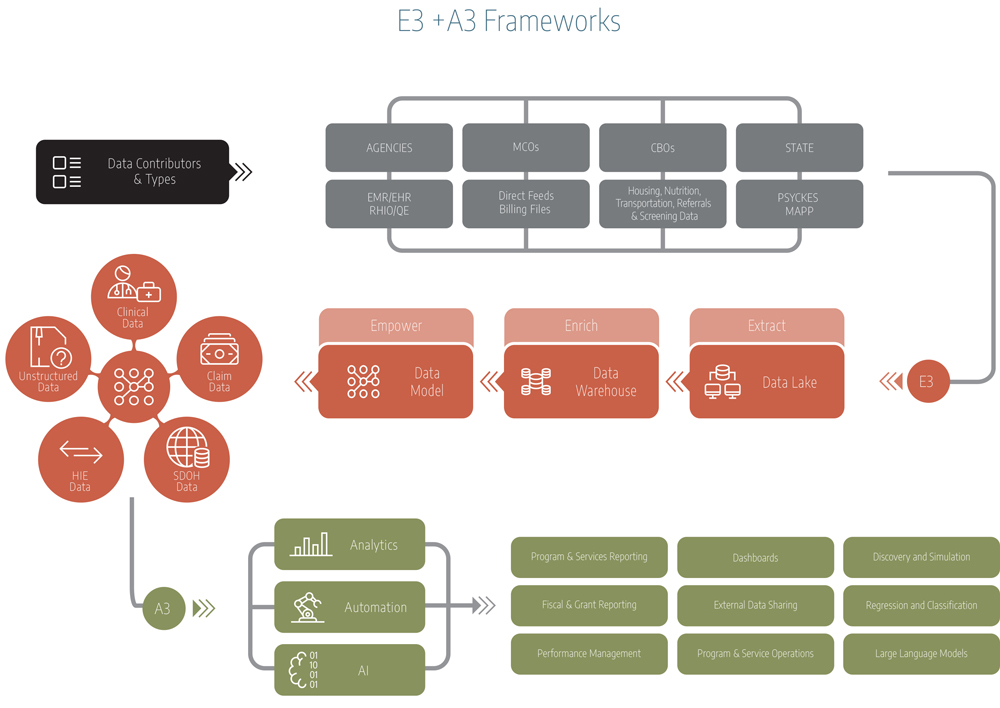
Informd aggregates and automates data in service of performance and quality reporting. Our E3 + A3 Frameworks turn information into insights.
Looking ahead – Moving CBC from BI to AI
The next phase of this transformation will focus on making the most of CBC’s unified data model to drive more advanced data science applications and show the real impact of integrated behavioral care. By deploying regression analysis, risk stratification, and classification techniques to their data store, CBC will help its providers and partners gain a deeper understanding of individual patient risks and develop tailored care plans.
Further, CBC believes that shifting from reactive to proactive care is the key to addressing the complex needs of today’s populations. Digital pathways and predictive analytics will play a crucial role in supporting decision-making and enabling earlier interventions. Looking ahead, CBC and Informd see the system continuing to evolve, with large language models (LLMs) enhancing care recommendations and reducing administrative tasks, making it easier for providers to deliver high-quality, whole-person care.
Pamela Mattel is CEO and Ashley Loser is Product Manager of Data Operations at Coordinated Behavioral Care. Maria Kordit is Engagement Director, Jason Lippman is Director of Development and Growth, and Jawad Sartaj is CEO of Informd.